India gets first liquid-mirror telescope that will track space debris, asteroids
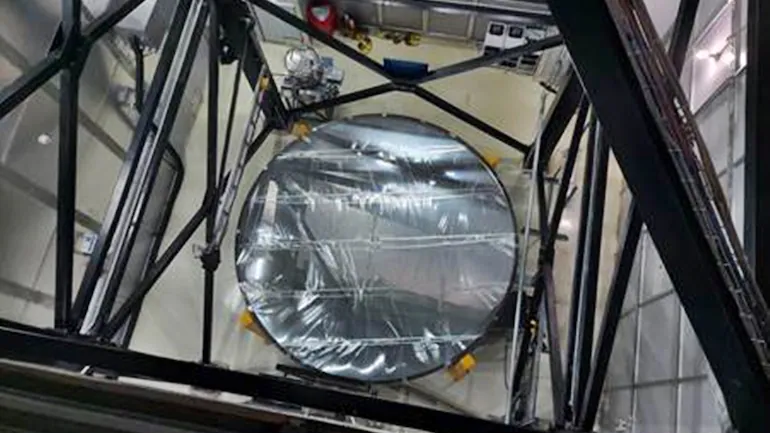
NEW DELHI: India has commissioned a unique liquid-mirror telescope atop a mountain in the Himalayan region that will keep a watch on the skies to identify transient or variable objects such as space debris, asteroids, supernovae and gravitational lenses. It is the country’s first and Asia’s ’s largest liquid-mirror telescope.
The telescope, built by astronomers from India, Belgium and Canada, is located at an altitude of 2,450 metres at the Devasthal Observatory campus of Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) in Nainital district, Uttarakhand.
Key Highlights about ILMT?
- It has become the world’s first Liquid-Mirror Telescope (LMT) to be commissioned for astronomy and also one of its kind to be operational anywhere in the world.
- Asteroids, supernovae, space debris and all other celestial objects will be observed using ILMT from an altitude of 2,450 metres in the Himalayas.
- Previously built telescopes either tracked satellites or were deployed for military purposes.
- ILMT will be the third telescope facility to come up at Devasthal.
- Devasthal is one of the world’s original sites for obtaining astronomical observations.
- Devasthal Optical Telescope (DOT) and Devasthal Fast Optical Telescope (DFOT) are the other two telescope facilities at Devasthal.
- In October 2022, full-scale scientific operations of ILMT will be started.
- It will be working along with India’s largest operating Devasthal Optical Telescope (DOT).
- The countries involved in ILMT’s development are India, Belgium, Canada, Poland and Uzbekistan.
How is LMT Different from Conventional Telescope?
- A LMT is a stationary telescope whereas a conventional telescope moves along the direction of the object of interest in the sky.
- A LMT will survey and capture any and all possible celestial objects such as stars, galaxies, supernovae explosions, asteroids and even space debris. However, a conventional captures just a piece of sky at a given point of time.
- LMT comprises mirrors with a reflective liquid (ILMT has mercury as reflective liquid). On the other hand, a conventional telescope uses highly-polished glass mirrors.
- While ILMT will be capturing images of the sky on all nights, conventional telescopes observe specific objects in the sky for fixed hours only.
Significance of ILMT?
- Enormous amount of data (10-15 GB/night) will be generated. This will be significant for the global scientific communities.
- Latest computational tools, like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and big data analytics will be deployed for screening, processing and analyzing the data.
- Selected data can be used as a base data for carrying out further focused research using spectrographs, near-Infrared spectrograph mounted on the in-house DOT.